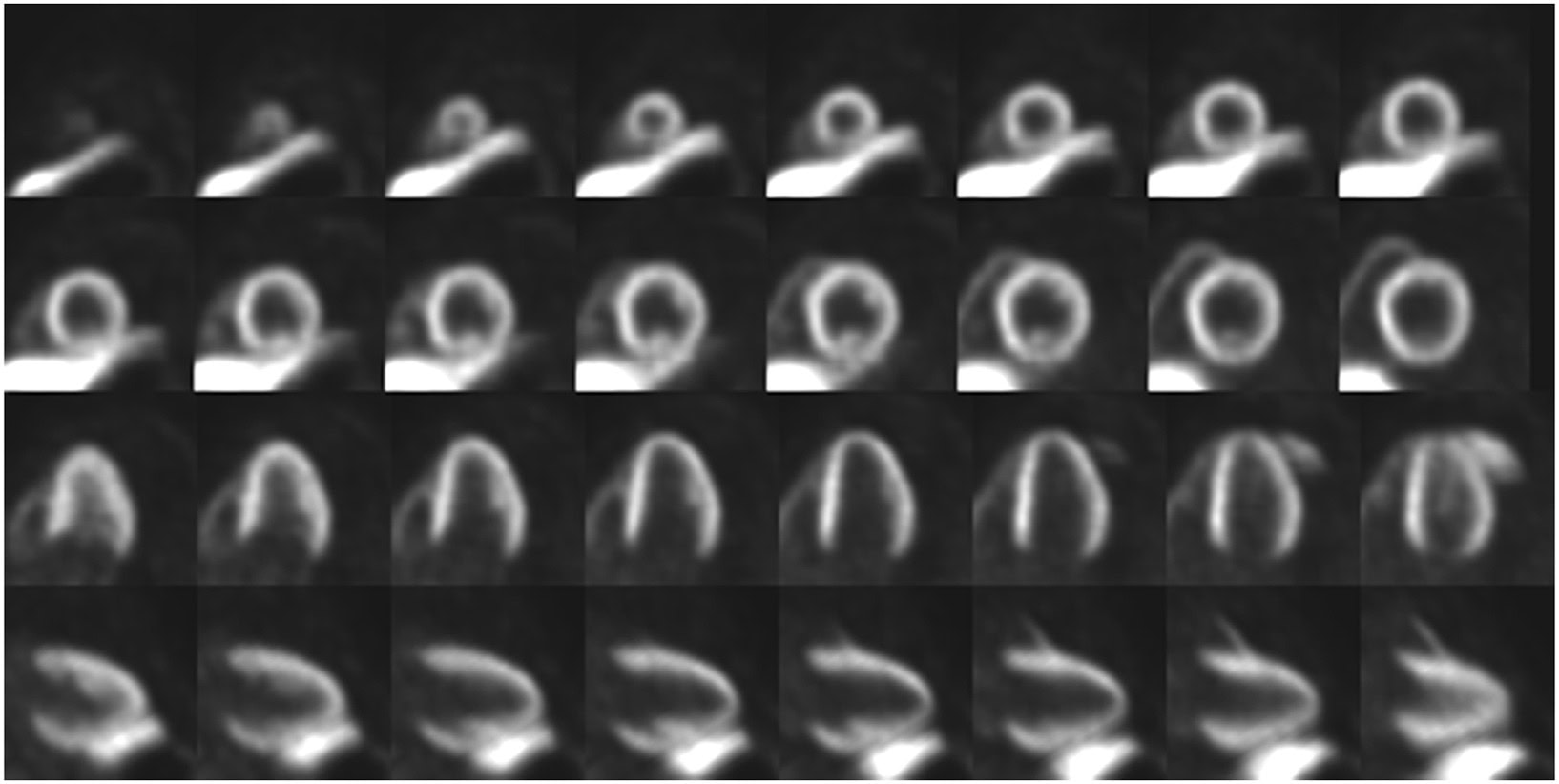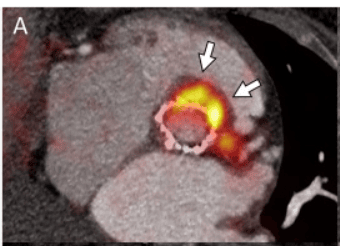
“XTR003, a Fatty Acid Metabolism PET Tracer: A Phase I Study to Evaluate the Safety, Biodistribution, Radiation Dosimetry, and Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Volunteers” is published in the April 2025 issue of the Journal of Nuclear Cardiology.
The nuclear cardiology pipeline includes several new radiopharmaceuticals, including the novel F-18-labeled PET tracer XTR003. A Phase I study published in the Journal of Nuclear Cardiology found XTR003 is safe and provides favorable imaging properties for assessing myocardial fatty acid metabolism. Tiantian Mou, PhD, and co-authors say a Phase II clinical trial evaluating the radiotracer’s efficacy is warranted.
More Highlights from the April 2025 JNC
Could CAD Provide a Roadmap for Nuclear Cardiology to Improve PAD Care?
The challenges currently associated with evaluating peripheral artery disease (PAD) “were similarly present for coronary artery disease (CAD) decades ago,” write Santiago Callegari, MD, and colleagues in a state-of-the-art review article. The authors detail the results of early perfusion imaging studies of PAD and postulate that nuclear cardiology’s experiences evaluating CAD could be applied to improve the care of patients with PAD.
ASNC/IANC-Funded Research Published in JNC
The Editor’s Choice study in the April 2025 JNC was funded in part by the ASNC/Institute for the Advancement of Nuclear Cardiology (IANC) Research Fellowship grant awarded in 2020 to the study’s lead author, Sanjay Divakaran, MD, MPH, FASNC. The findings suggest that post-exercise PET imaging with skeletal muscle blood flow measurement could provide physiologically relevant information for assessing peripheral artery disease (PAD) and guiding treatment. In an accompanying editorial, Neela D. Thangada, MD, says the study “adds to the growing body of literature on skeletal muscle microvascular perfusion in people with PAD.”
If you are already logged into your ASNC account, access JNC here.
Article Type
JNC News
Category
Journal of Nuclear Cardiology (JNC), Research
Related Posts
Step-by-Step Guide to PET/CT Interpretation in PVE
Now that 18F-FDG-PET/CT has a class 1 indication for evaluating suspected prosthetic…
ASNC/IANC-Funded Research Published in JNC
The April issue of the Journal of Nuclear Cardiology includes original research,…
First JNC Compendium Focuses on Potentially Transformative Impact of F-18 Flurpiridaz
The Journal of Nuclear Cardiology just published the inaugural JNC Compendium, a…